LINE
Lines are everywhere. You can see lines in the grain of a piece of wood or in the cracks on a sidewalk.
In art, Line is an element of art that is the path of a moving point through space.
Lines are used to:
• Create boundaries between shapes
• Create boundaries between colours, textures or values
• Lead the eye from one space to another
• Create textures
• Suggest emotional qualities
Lines can VARY in 5 ways: length, width, texture, direction and degree of curve.
Implied lines are a series of points that the viewer’s eyes automatically connect. Implied lines are suggested rather than real lines; a series of dots or dashes or a trail of wet footprints can create an implied line.
The 5 Basic Kinds of Lines are: vertical, horizontal, diagonal, curved and zig-zag
• Vertical and Horizontal lines are considered static. Vertical can show dignity and formality. Vertical express feelings of peace and stability.
• Curved, Diagonal and Zig-Zag are considered active. Curved lines express activity. The larger the curve, the calmer the line appears. A spiral can be hypnotic.
• Diagonal lines express instability, tension and excitement. Zig-zag lines can create confusion and intensity.
SHAPE
Rocks, puddles, flowers, shirts, houses, chairs, and paintings are all shapes and forms.

A Shape is a two dimensional area that is defined in some way. It may have an outline or a boundary around it or you may recognize it by its area.
Shapes are geometric or free form (organic)
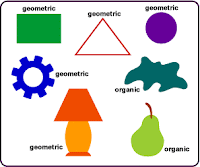
• Geometric shapes are precise shapes that can be described using mathematical formulas (square, rectangle, triangle, circle, hexagon)
• Free form shapes are irregular and uneven shapes. They often occur in nature. We can also call them organic; a leaf, a puddle.
FORM
A form is an object that has 3 dimensions. Like shapes, forms can be geometric or free form. Like shapes, they have length and width, but forms also have depth.
LENGTH + WIDTH + DEPTH
There are many categories of forms. Architectural forms refer to buildings. Natural forms occur in nature. Geometric forms have a geometric shape as a base. Abstract forms can also be called free from or geometric and have no reference to any geometric shape. Realistic forms are 3D objects which may be geometric or freeform, but is a recognizable form, such as a chair.
Shapes can become Forms with shading or perspective. A circle can become a sphere or a cylinder. A square becomes a cube. A triangle becomes a pyramid or a cone.
SPACE
Space is the element of art that refers to the emptiness or area between, around, above, below or within objects. All objects take up space. You, for example, are a living, breathing form moving through space.
 In 2D and 3D art, we call the shape or form positive space. The empty spaces around the shape are called negative space.
In 2D and 3D art, we call the shape or form positive space. The empty spaces around the shape are called negative space.In 2D art, artists use space to create an illusion of depth.

Changes in value: the closest area is the brightest while the shaded or dark areas show areas farther away.
Colour: the brightest is the closest, the dullest or lightest further away.
Detail: objects with clear sharp edges and visible details seem closer than blurred or hazy forms in the distance.
Overlapping: when objects are partially obscured by other objects in front of them, we think they are further back.
Perspective: 1 point, 2 point and 3 point defines space using a horizon line and a vanishing point.


TEXTURE
Texture refers to how things feel or look as if they might feel if touched.
Some adjectives used to describe textures are smooth, soft, fine, rough, fuzzy, sharp, prickly, billowy, hard, bumpy.
When you actually touch something it is called tactile or actual texture. You can touch the texture of a smooth surface or an uneven rough surface of a painting.
A collage is a picture created with many different types tactile texture.
When you see something and you can guess or remember how those objects feel, that is visual or simulated texture; the illusion of a three dimensional surface.
The artist tries to draw or paint objects so that they appear to have texture. He/she will attempt to make the silk look shiny or a rock look rough and coarse. Artists do this in 2D art using various types of marks, techniques, tools and media.
Some ways of creating texture are: Cross-hatching, Hatching, Textural Marks, Spattering, Pointillism, Lines, Sponging, Frottage, Smudging
VALUE
Value is the amount of light reflected from an object’s surface and is represented by varying amounts of lightness and darkness.
It can be controlled by either adding white or black to create tints or shades or by adding its complement to a colour to reduce its brightness.
Value can be used to change a flat 2D shape into a 3D form. Objects are generally lightest at the part closest to the light source, and become darker as they recede from the light. If an object is rounded, the value will gradually change from light to dark.
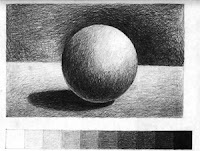 In drawing, Value can be added by using: lines of value scale in shading, hatching, cross hatching, stipple…
In drawing, Value can be added by using: lines of value scale in shading, hatching, cross hatching, stipple…A Value Scale can be used to test a medium for range of values.
To lighten add WHITE, this is called TINTING
To darken add BLACK, this is called SHADING
To darken add BLACK, this is called SHADING
COLOUR
 Colour is everywhere.
Colour is everywhere. We see it in the blue of the sky, the yellow, reds and oranges of the changing autumn leaves, the green of the grass, and the black of the night.
The Colour Wheel is an effective way of organizing colours.
Primary colours are pure colours and cannot be made by mixing from any other colour. Red. Blue. Yellow.
Secondary colours are created by mixing two of the primary colours together. Orange. Green. Purple.
Mix each primary colour with its neighbouring secondary, and the result is a Tertiary colour; yellow-green. yellow-orange.
A hue is the name of a colour in the colour spectrum, such as red, blue, or yellow.
A shade is a colour with black added to darken it. A tint is a colour with white added to lighten it.
Cool colours have the root of blue, suggesting coldness: mixtures of blue, green or purple
Monochromatic is one colour plus white and black
Complementary Colours are opposite each other on the colour wheel. Red and Green. Yellow and Purple.















No comments:
Post a Comment